What is UDI?
- D.I. is a healthcare part of Traceability, which helps to trace back the product.
- D.I. Stands for Unique Device Identification, which are directives for Standardized labeling for medical devices to be marketed in U.S. and E.U.
- These directives are released by U.S. F.D.A. (Food and Drug Administration) and issued by FDA accredited agencies namely: -
- GS1
- HIBCC (Health Industry Business Communications Council)
- ICCBBA (International Council for Commonality in Blood Banking Automation)
- D.I. Labeling is done with accordance to the importance or the risk involved in the medical instrument to be used.
- D.I. directives thus categorized the medical devices into three classes according to risk factor and control needed.
U.D.I Risk Classification and Labeling:
In U.S.A. and E.U. according to U.D.I. directives medical devices are classified as:
|
Class |
Risk and Control |
Categories |
Marking System |
|
Class I |
Low risk and Easy Control devices |
Surgical scissors, Stethoscopes, Syringes, Bandages |
Labels on packaging |
|
Class II |
Moderate risk and general/ special control |
Powered Wheelchairs |
Direct Part Marking |
|
Class III |
High risk, Lifesaving/sustaining |
Pacemakers, Heart valve, Prosthesis, Bone-Screws. |
Direct Part Marking |
“Reusable devices which requires sterilization/disinfection needed U.D.I. to be direct part marked”.
Note: Your respective component that needs laser marking comes under CLASS-III category as per U.D.I norms.
Why U.D.I Marking:
- According to GS1 and McKinsey report 2012, "Implementing global standards across the entire healthcare supply chain could save 22-43,000 lives and avert 0.7 to 1.4 million patient disabilities on an annual basis.”
- Motto of U.D.I. agencies is “right patient, right drug or device, right time, right dose, right route”
- These global healthcare standards thus help in:
- Enabling verification of Patient Identity
- Enabling product verification ensuring that the right patient receives the right medication.
- Efficient product recalls by linking the medical product to the patient.
U.D.I Marking Format?
- FDA approved issuing authority to the manufacturers issues the U.D.I code.
- The codes are represented in two forms*
- Easily readable alphanumeric characters (HRI/Human Readable Interpretation)
- AIDC technology (Automatic Identification and Data Capture), which means a machine-readable code (barcode/2D code). {*A/t 21 CFR 801.40}
- The code format consists of:
D.I. (Identify labeller & Specific Device ) = Device Identifier + P.I.( Identify: Lot number, Manuf. Date, Expiry Date, Serial No. ) = Production Identifier
Note: The DI is a globally unique product code, which allows for the clear identification of a device.]- Contains static information.
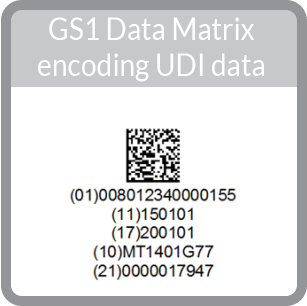 |
 |
GS1 Format
WHY URSA: MEDILASER 2-Axis FOR U.D.I MARKING:
One of the major challenges facing UDI is the implementation of the appropriate direct marking technology. Moreover, not every method is suitable for secure and UDI-compliant direct part marking; therefore, choosing the best method to meet the requirements can be difficult and is crucial.
This machine is specially designed to comply as per UDI Directives in accordance to SFDA-GS1.
|
|
LASER MARKING |
|
MARKING CHARECTERISTICS |
|
|
Good readability/high quality |
YES |
|
Machine readable |
YES |
|
High contrast |
YES |
|
Permanent and erosion resistant |
YES |
|
Biocompatible |
YES |
|
Resistant to acids, solvents, cleaning and sterilization |
YES |
|
Corrosion resistant# |
YES |
|
Passivation process# |
YES |
|
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE MARKING PROCESS |
|
|
Easy application of variable data, codes, series production |
YES |
|
Consumables |
NO |
|
Low maintenance, low wear |
YES |
|
Adjustable marking size |
YES |
|
Does not damage material |
YES |
|
Marking of uneven surfaces |
YES |
Advantages of Laser Marking:
- Validated and tested marking for sterilization
- Process reliability, Efficient and streamlined production
- Error-Free marks
- Reliable Traceability
- Secure markings as required by medical standards
#Depend upon material composition and additional passivation process may be recommended, trials to be carried out on actual material sample before confirmation (material composition differes from suppliers to suppliers)
Key Points of URSA: MEDILASER 2-Axis for medical industry:
Technical Competence:
The Machine
- The machine has the capacity to do the following functions:
- Parameter Finder: Easy to find which parameters suits best on your substrate.
- Standard recommended parameters on different substrates
- High contrast black markings* that are resistant to corrosion (optional Passivation)
- Markings done on medical components by our URSA: MEDILASER 2-Axis can sustain >50 autoclave cycles#
- Markings pass salt spray test as per ISO norms#
- Integrated panel A/C for maintaining the optimum system working temperature.
- Integrated Barcode Scanner with ability to provide code quality grade along with reports.
The BRAIN
Traceability & Data Management Software: Customized Graphic User Interface for Medical Industry.
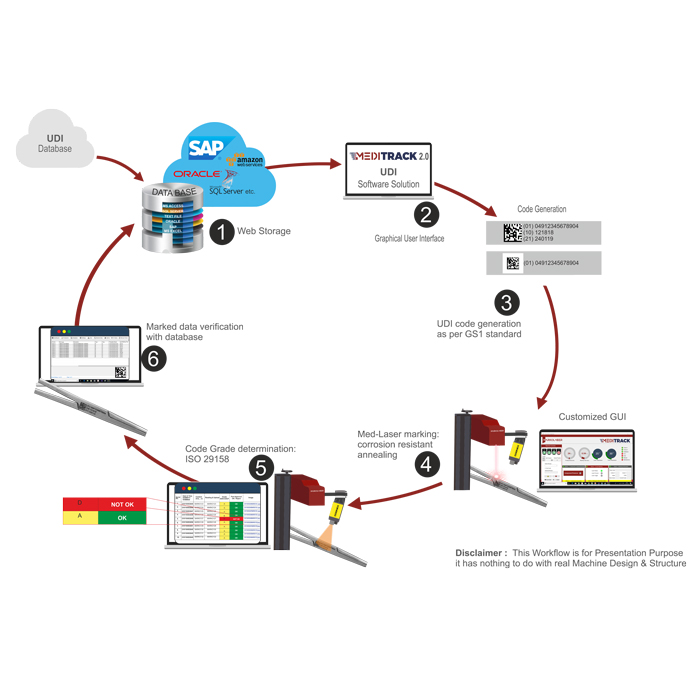
Machine process flow:
- MARKOLASER provides customized individual interfaces programmed by MARKOLASER experts for implementing the traceability of medical devices in respect to U.D.I norms or can integrate existing database as per customer requirements. Other than data input through databases, the data can also fetch through external scanners.
- The MEDITRACK 2.OClient Control Interface connects the online or offline databases with the marking laser.
- The MARKOMARK: Laser Marking Software generates the code from the relevant UDI-data as per UDI norms.
- The URSA: MEDILASER2-Axis marks the relevant UDI data onto the Class-III medical devices with a high-contrast, permanent marking, which can still be read by both humans and machines even after numerous cleaning cycles#.
- The subsequent quality & verification process is made easy with-in built
- COGNEX DPM reader. The in-built COGNEX reader allows UDI-Compliant codes to be recognized, read out, and be subjected to a quality assessment.
- The marked data on the component is compared with the data present in the database for accuracy. Finally, the grade of the code marked on the component is checked and the same is stored in the database along with other process parameters e.g. time, operator, and parameters for future use.
- Defective markings are identified and are separated from the good ones.
Kindly, find the below mentioned pictorial process flow chart for better understanding.
*The contrast of marking may depend on the type of metal used. High contrast black markings are possible on certain metals.
#The tests done are in-house and on our own substrates, it is highly recommended that the concerned person performs these tests in their own laboratory.

